Distribution or Transfer of Commodity Codes to Feeder System Using ALE Change Pointers From SAP GTS E4H
Commodity codes classify goods for customs, tax calculations, and compliance in international trade. SAP Global Trade Services (SAP GTS) Edition for HANA enables the efficient transfer of these codes to feeder system such as SAP S/4HANA and SAP ERP feeder systems using Application Link Enabling (ALE) change pointers. This guide explains the distribution process and how to ensure seamless updates.
Commodity Code Usage:
- Used in both SAP GTS and Feeder System SAP ECC or SAP S/4 Hana
Creation & Transfer:
- Can be created in the Feeder System and transferred to SAP GTS.
- Can also be created in SAP GTS and transferred to the Feeder System.
- Best Practice: Create in SAP GTS and transfer to the Feeder System.
Transactions Prior to S/4 HANA 1610:
- /SAPSLL/SWNAV_RTR,
- /SAPSLL/SWNAV_DISP
- /SAPSLL/SWNAV_RTR_R3
For details process you can follow this link
Transactions After S/4 HANA 1610: which ALE based.
- /SAPSLL/COMCO_RTR
- /SAPSLL/COMCO_RTR_IN
In this blog we will discuss only ALE change pointer commodity code transfer or distribute to Feeder system.
What Are ALE Change Pointers?
ALE (Application Link Enabling) facilitates data exchange between SAP systems. Change pointers track modifications and ensure only necessary updates are sent to connected systems, keeping commodity codes synchronized without excessive data transfer.
A. Configuration in SAP GTS E4H
Activating Change Pointers
- T.Code [BD61]
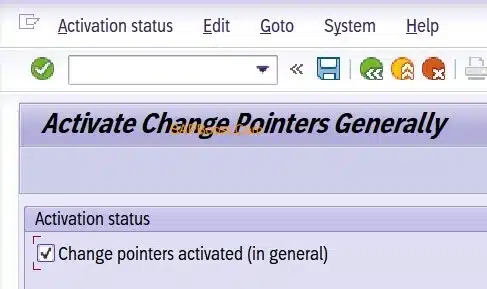
- Change pointers track modifications to commodity codes.
- Only relevant changes are recorded for distribution, minimizing system load.
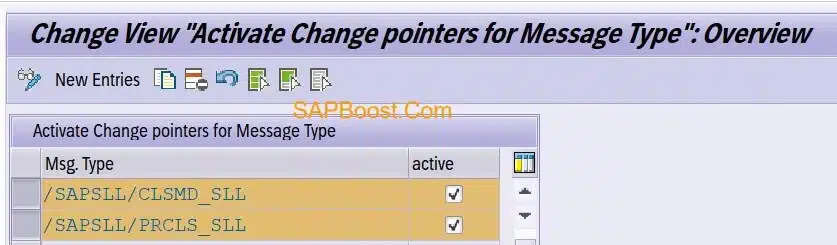
Activate Change Pointers For Message Types.
- T.Code:- BD50
- Add Message types and Activate.
- /SAPSLL/CLSMD_SLL:- Message type: Contains changes to classification master data
- /SAPSLL/PRCLS_SLL:- Message type: Contains classification changes
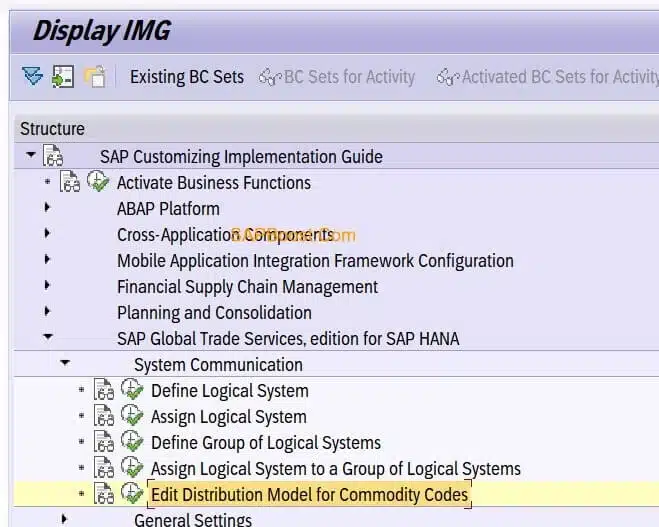
Maintain ALE Distribution Model
- Path:- SPRO -> Customizing: Global Trade Services –> System Communication -> Edit Distribution Model for Commodity Codes.
- Create Model
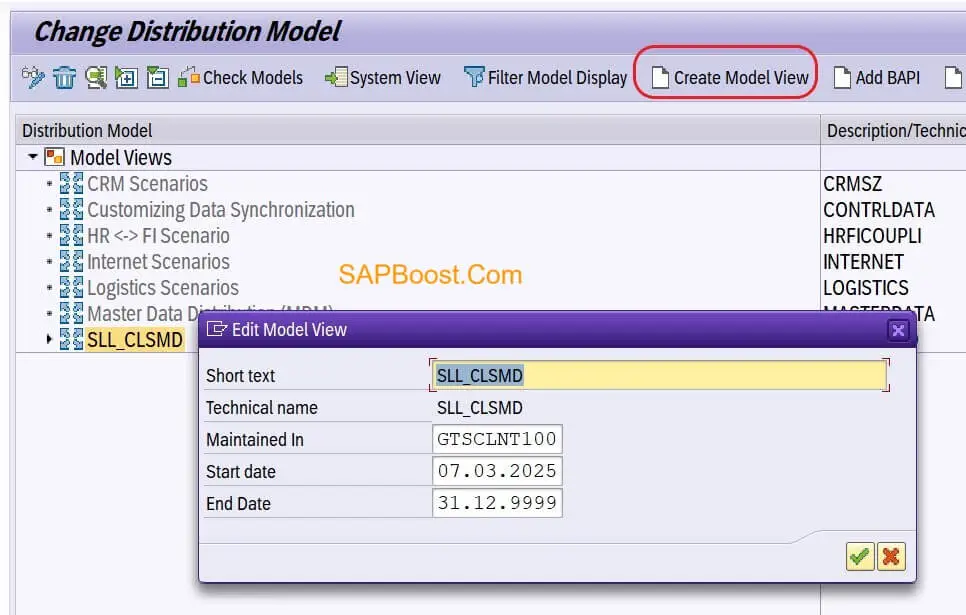
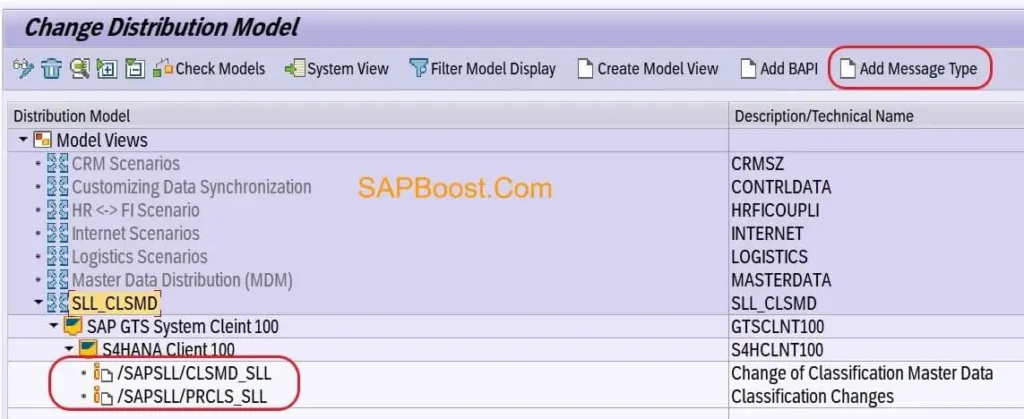
- Add above TWO message types like above screen shot.
Activate Numbering Scheme for Distribution
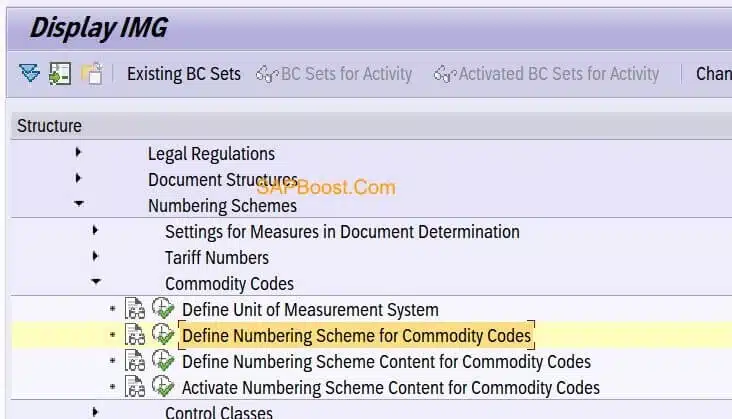
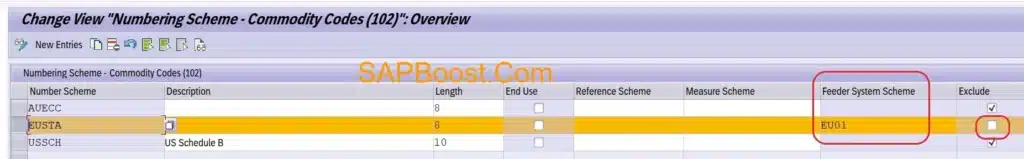
- Deselect Exclude Check box so that respective number scheme will be used to transfer to feeder system.
B. Configuration Commodity Code in SAP Feeder System.
- Path:- SPRO -> GRC -> International Trade -> Classification -> Commodity Code
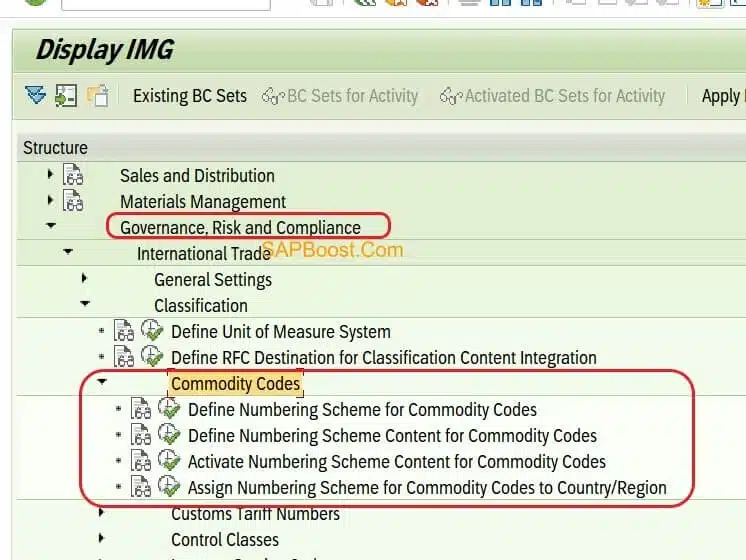
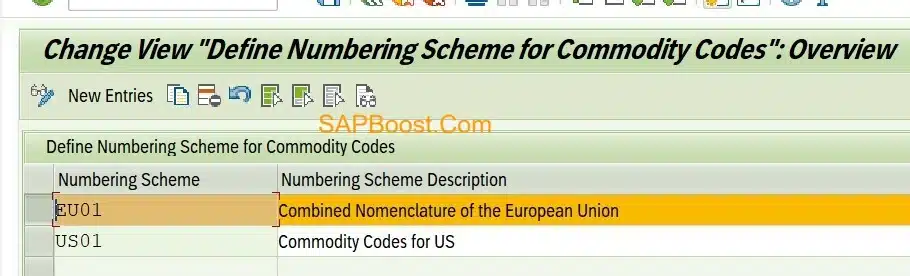
Define Numbering Scheme for Commodity Codes
Define Numbering Scheme Content for Commodity Codes
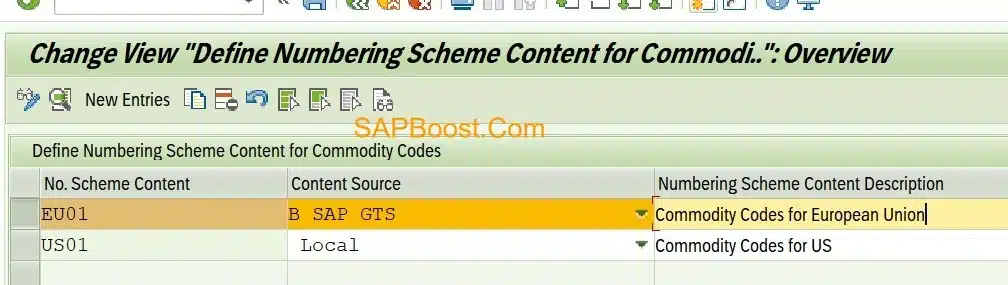
- Content source should be “B:- SAP GTS”
Activate Numbering Scheme Content for Commodity Codes
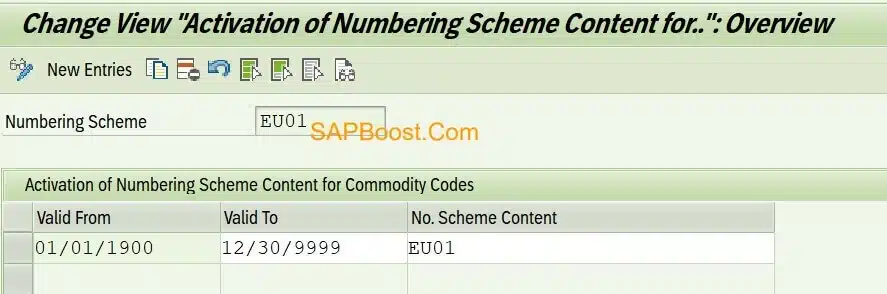
- Assign Scheme Content under numbering scheme.
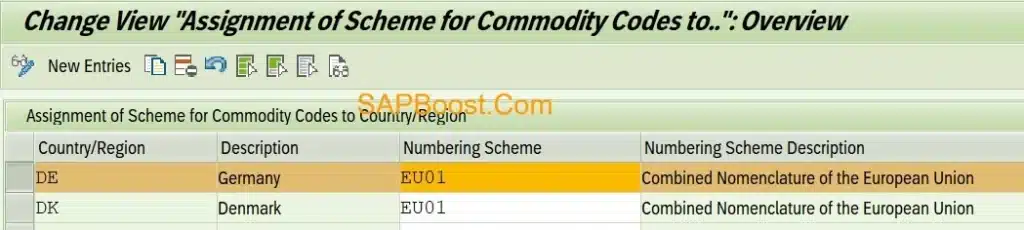
Assign Numbering Scheme for Commodity Codes to Country/Region
C. Manually Transfer Commodity Code from GTS to Feeder System
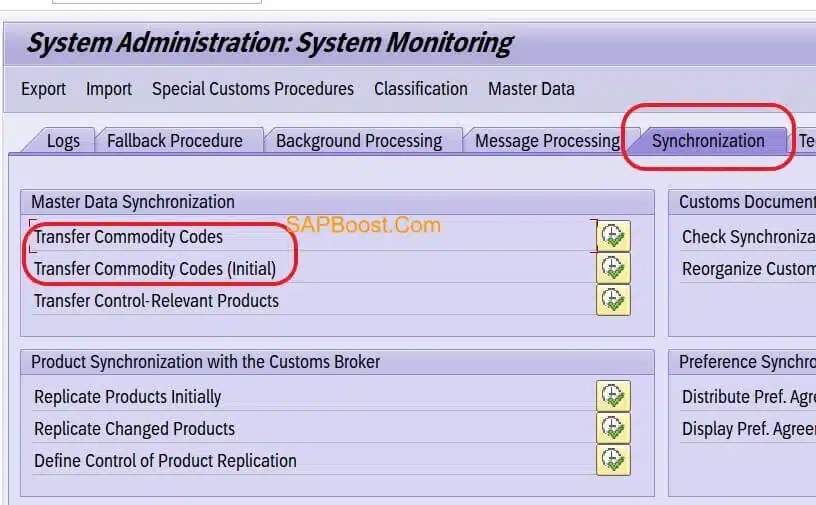
Transfer Commodity Codes (Initial)
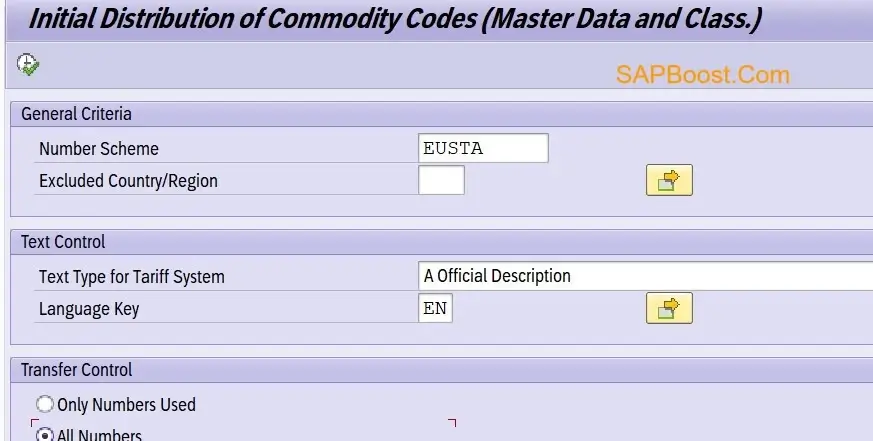
- Fill Numbering scheme.
- Click on Execute Button
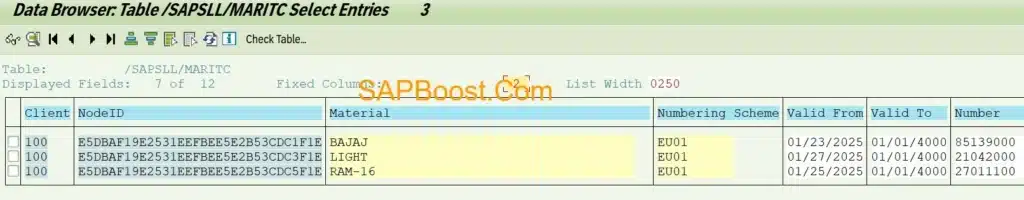
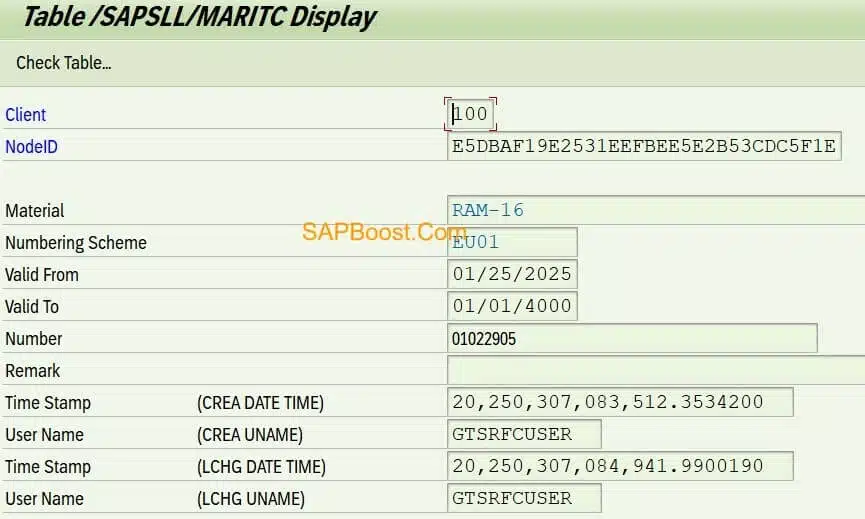
Material Trade Classification:- /SAPSLL/MARITC table in Feeder System
Trade Classification Number /SAPSLL/CLSNR
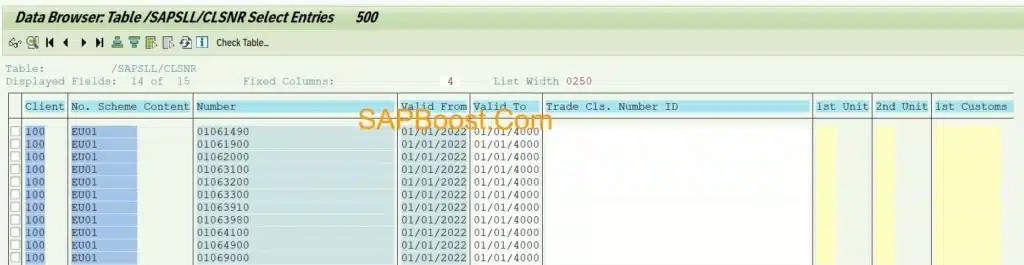
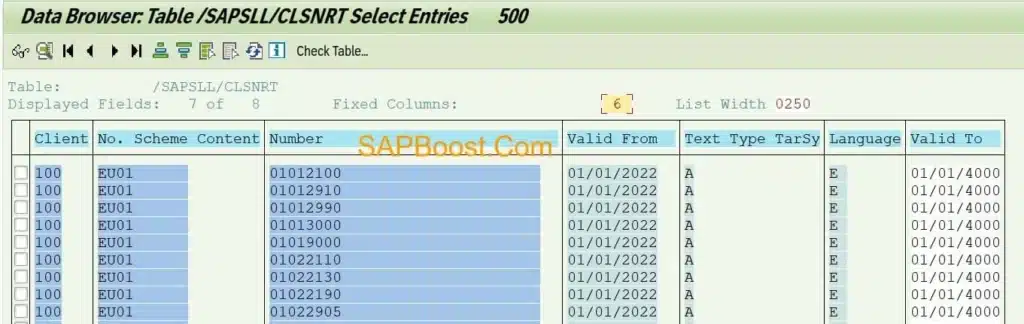
Description of Trade Classification Number – /SAPSLL/CLSNRT
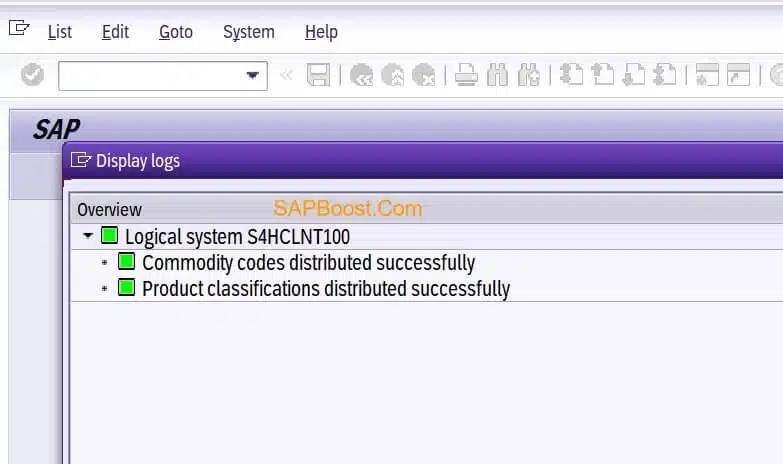
Transfer Commodity Codes from GTS to Feeder System /SAPSLL/COMCO_RTR
Reclassify the product to capture change pointer
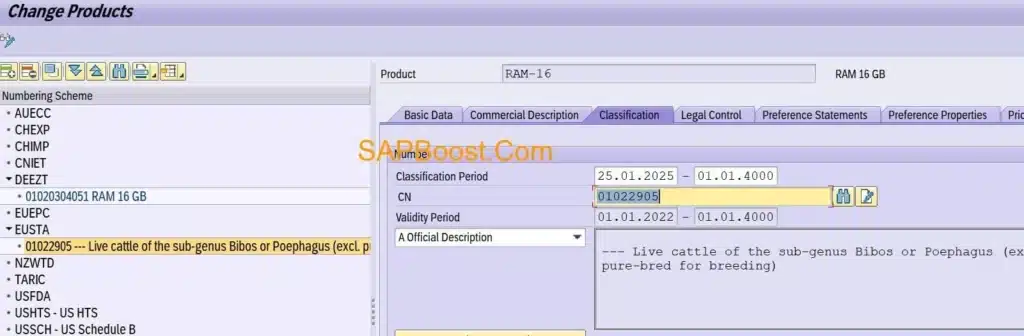
- Material is classified with new commodity code which will be captured in change pointer.
Transfer Commodity Codes
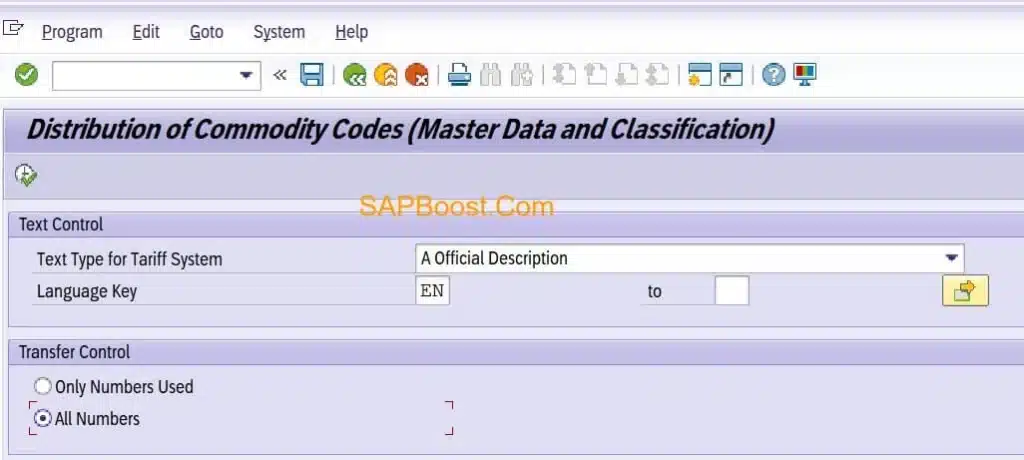
Material Trade Classification:- /SAPSLL/MARITC table in Feeder System
Benefits of ALE Change Pointers for Commodity Code Transfer
- Efficiency: Transfers only relevant updates, reducing system load.
- Accuracy: Minimizes manual effort and errors.
- Compliance: Keeps all systems aligned with trade regulations.
- Automation: Enhances operational efficiency by automating updates.
Conclusion
Using ALE change pointers ensures smooth and accurate distribution of commodity codes from SAP GTS to SAP ERP and S/4HANA. This method improves efficiency, compliance, and automation in trade classification. Proper monitoring and troubleshooting help maintain seamless integration, ensuring businesses stay up to date with regulatory changes.
Join Our SAP SD & GTS LinkedIn Group
